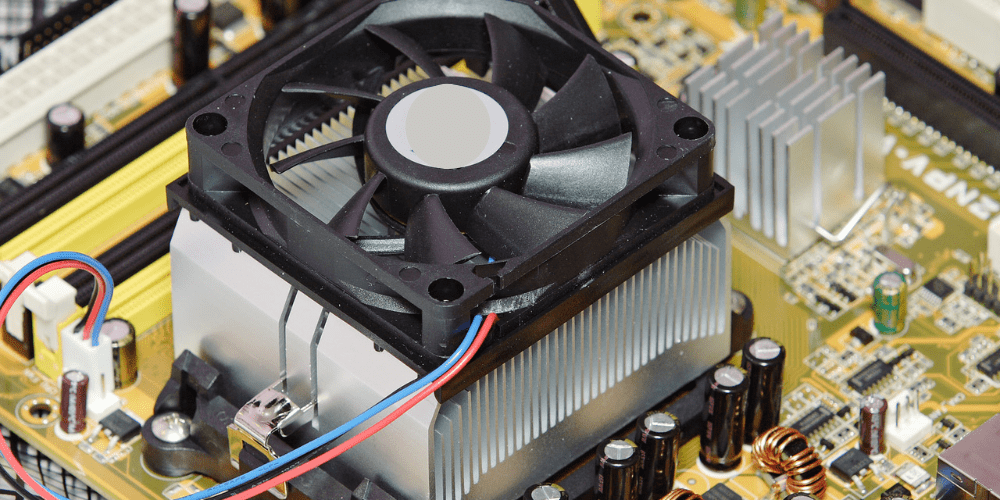
Firstly, a thermal heat sink is a type of heat sink designed specifically to dissipate heat from electronic devices. And other types of heat sinks, such as heat sinks used in HVAC systems or in automobiles, have different designs and purposes. Here are some of the main differences between thermal heat sink and other types of heat sinks:
- Design: Thermal heat sinks are designed to be compact and lightweight, with a high surface area-to-volume ratio to maximize heat dissipation. Other types of heat sinks, such as those used in HVAC systems or automobiles, may have different shapes and designs to meet their specific requirements.
- Material: Thermal heat sinks are typically made from materials such as aluminum or copper with high thermal conductivity. Other types of heat sinks may be made from different materials depending on the specific application.
- Thermal Resistance: Thermal heat sinks are designed to have low thermal resistance, which allows them to transfer heat away from the electronic device efficiently. Other types of heat sinks may have higher thermal resistance, which can be acceptable for their specific applications.
- Attachment Method: Thermal heat sinks are typically attached directly to the electronic device using a thermal interfaces material such as thermal paste or adhesive tape. Other types of heat sinks may be attached differently, such as being mounted to a heat exchanger or radiator.
- Overall, thermal heat sinks are specifically designed for electronic devices and have unique features that make them different from other types of heat sinks. Their compact size, high surface area, and low thermal resistance make them an effective solution for dissipating heat from electronic devices.
Increased efficiency of thermal heat sinks in electronic devices:
Is there a solution to improve the overall efficiency of thermal heat sinks in electronics? Well, yes. There are several ways to increase the efficiency of thermal heat sinks in electronic devices:
- Increasing Surface Area: One way to increase the efficiency of a thermal heat sink is to increase its surface area. This can be done by adding fins or other features that increase the amount of surface area exposed to the air. This allows for more heat to be transferred from the heat sink to the surrounding air.
- Using Higher Thermal Conductivity Materials: Using materials with higher thermal conductivity can increase the efficiency of a thermal heat sink. Materials such as copper or silver have higher thermal conductivity than aluminum, commonly used for heat sinks. Using these materials can allow for more heat to be transferred from the electronic device to the heat sink.
- Using Heat Pipes: Heat pipes are a type of heat transfer device that can be used in conjunction with thermal heat sinks to increase their efficiency. Heat pipes work by transferring heat from the electronic device to the heat sink through a closed loop system. This can allow for more efficient heat transfer and can increase the overall efficiency of the thermal heat sink.
- Proper Mounting: Properly mounting the thermal heat sink to the electronic device is critical for increasing efficiency. This involves using a high-quality thermal interface material, such as thermal paste, to ensure good thermal contact between the heat sink and the electronic device. Additionally, ensuring that the heat sink is securely mounted to the device can prevent thermal resistance caused by air gaps or movement.
Regardless, increasing the efficiency of a thermal heat sink involves maximizing its ability to transfer heat away from the electronic device. This can be achieved through design features, material selection, the use of additional heat transfer devices, and proper mounting techniques.